In no specific order.
Concept Design and Economic Feasibility Study of a Modular
Underwater Apartment: A Case Study at Webb Institute
Ian Cavanaugh and Duane Lee
Underwater structures have already been proven to be an innovative solution in the luxury hotel/restaurant industries. This thesis explores if an underwater apartment is a feasible alternative housing option to address housing shortages around the world, especially for areas with rising sea levels. The concept design of the apartment is created with economic feasibility in mind to attempt to make this alternative housing option as affordable as possible while providing all necessities that a normal land house provides. To make this project as practical as possible, Webb Institute is used as a sample case study.
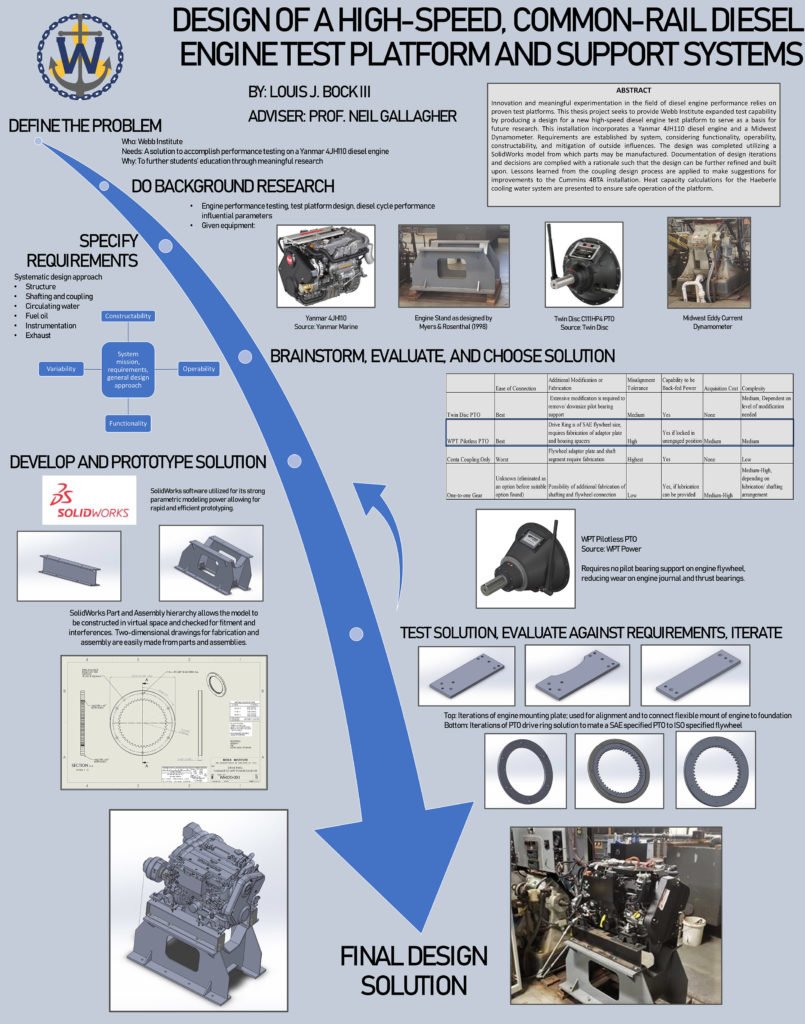
Design of a High-Speed, Common-Rail Diesel Engine Test Platform and Support Systems
Louis Bock
The diesel engine to this day remains the dominant source of marine propulsive power. However, the demand for improving efficiency and minimizing environmental impact has driven innovation towards newer technology. The objective of this project is to give Webb’s Haeberle Laboratory a modern platform, in the form of a Yanmar common-rail engine, to continue research into what is possible with a diesel engine. A 3D digital prototype is developed using SolidWorks from which part and assembly drawings can be derived for fabrication and installation. The comprehensive design of the platform ensures test results are accurate and repeatable. The design process is extensively documented; compiling the design rationale, tradeoff studies, design iterations, and models to allow for future modification and growth of the platform. Lessons learned through this design process are applied to make recommendations for functional improvements to the Cummins engine test platform already in use in Haeberle Laboratory.
Webb’s Open-Circuit Wind Tunnel: Setup and Best Practices
Alec Gonzalez
Wind tunnels are testing devices used to aid in flow visualization and to measure lift and drag forces of an object immersed in a fluid. The purpose of this thesis is to first complete the set up of Webb’s open-circuit wind tunnel, donated by Navatek. With the wind tunnel ready for operation, research of the best practices regarding wind tunnel testing is compiled to ensure proper use in the future. Topics included model similitude, turbulence stimulation, and blockage effects. Despite the information and conclusions drawn for similar wind tunnels, each wind tunnel and experiment must be considered individually, as there are no universal rules for wind tunnel experiments.
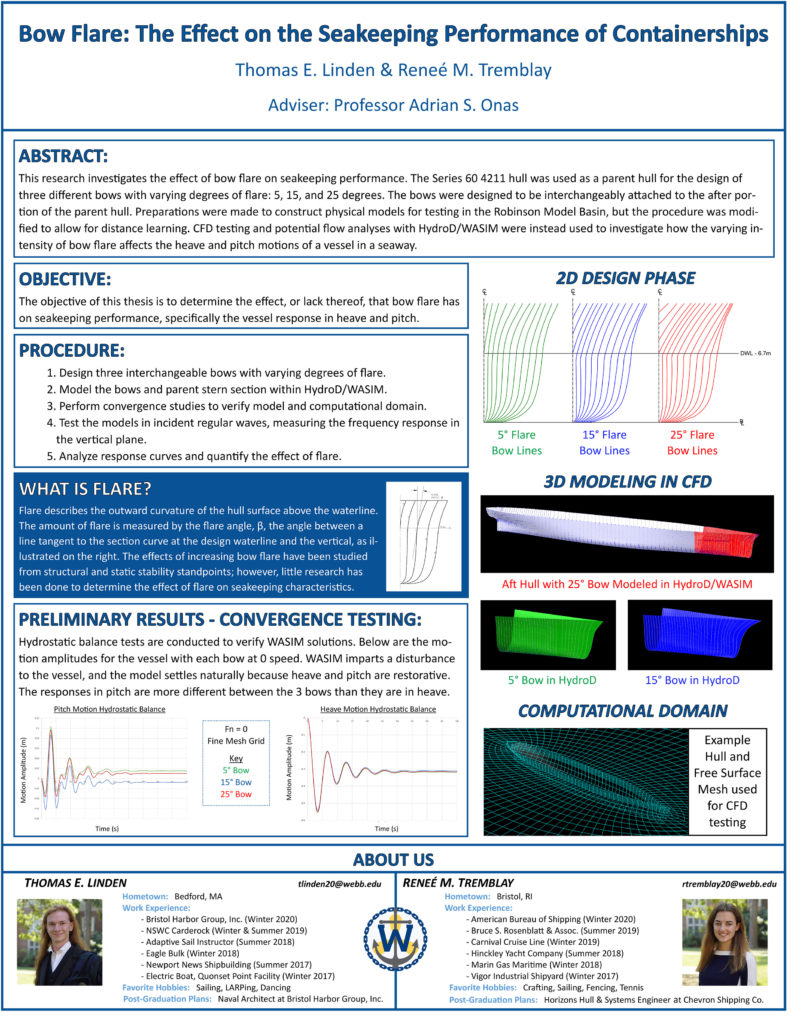
Bow Flare: The Effect on the Seakeeping Performance of Containerships
Tommy Linden and Reneé Tremblay
As containerships become larger and larger, the bow flare is often made more extreme to increase the width at the foredeck so that the vessel can carry more cargo on deck during a single voyage. While the effects of increasing bow flare have been studied from both structural and static stability standpoints, very little research has been done to determine the effect of bow flare on seakeeping characteristics. In this thesis, a model of a containership and three interchangeable bow pieces with varying degrees of flare are designed, modeled, and tested using the potential flow code, HydroD/WASIM. The frequency response curves (transfer functions) for pitch and heave are analyzed for a range of wave frequencies for each bow. The test data are used to determine the effect, or lack thereof, that bow flare has on seakeeping performance.
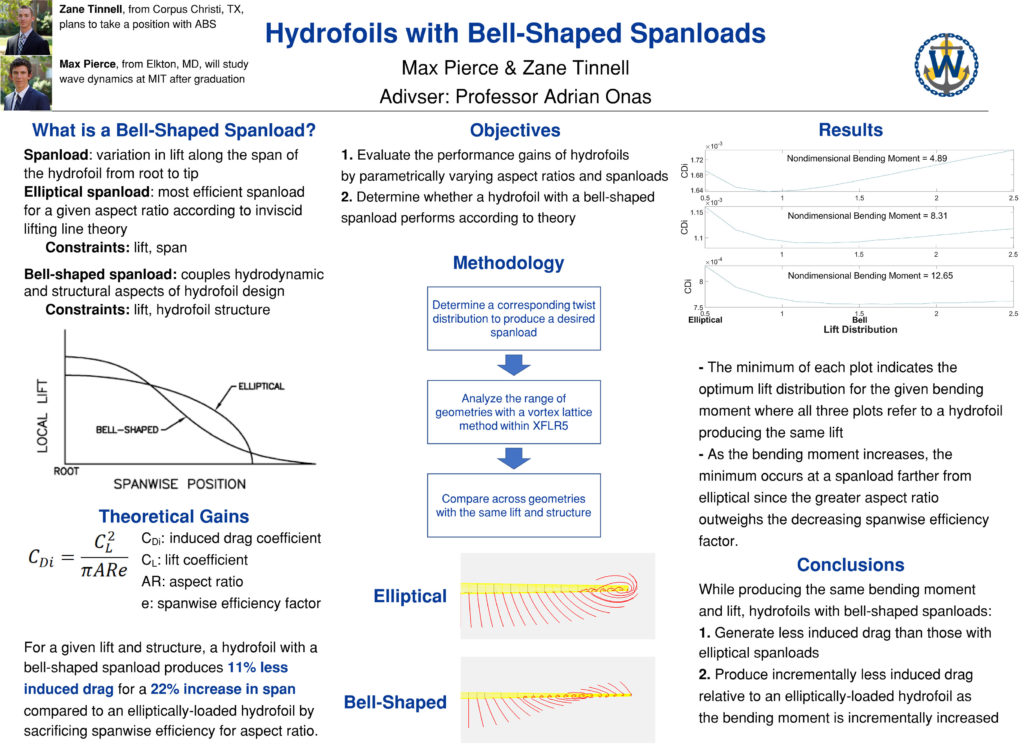
Effect of Nonlinear Geometric Twist on Hydrodynamic Performance of Hydrofoils with Bell-Shaped Spanloads
Max Pierce and Zane Tinnell
Departing from the elliptical spanload, which is the established benchmark for hydrofoil design, a bell-shaped spanload foil adheres to different constraints, which yield a geometry with better performance for a given amount of structure. The desired spanload is achieved by twisting the foil along its span, and the objective of the thesis is to study the effects of varying degrees of twist on foil performance. Various geometries will be tested in the Webb flow channel, using both conventional load measurement and particle image velocimetry.
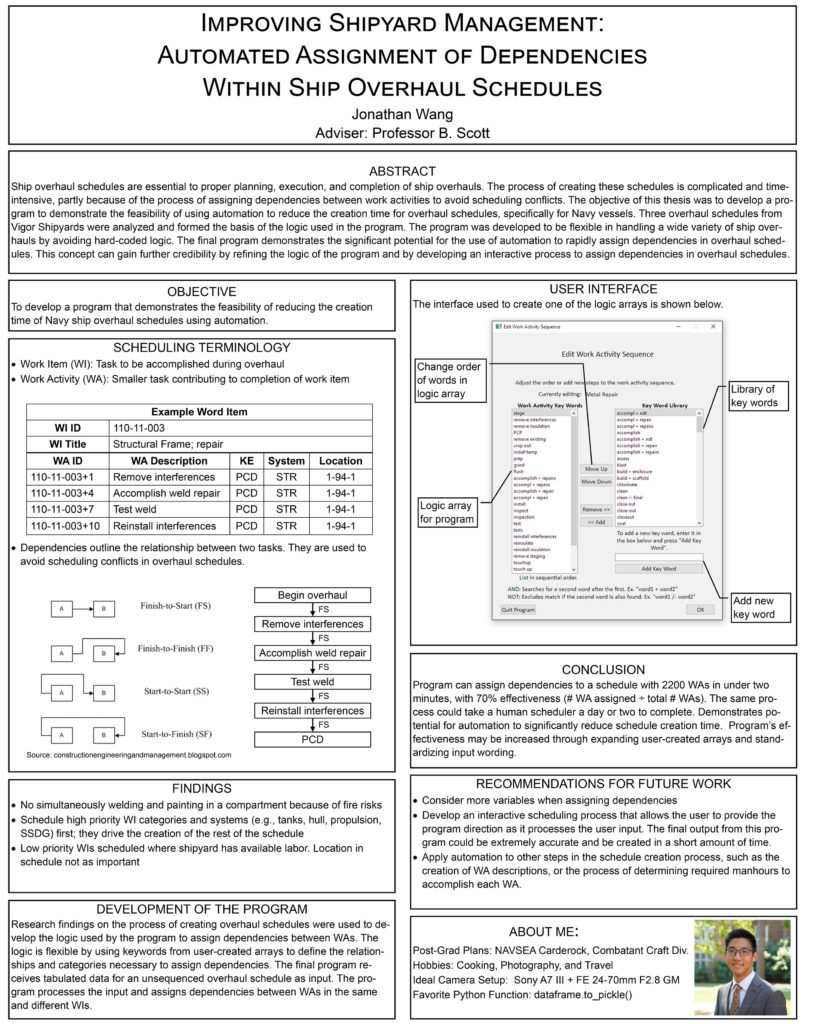
Improving Shipyard Management: Automated Assignment of Dependencies Within Ship Overhaul Schedules
Jonathan Wang
Ship overhaul schedules are essential to proper planning, execution, and completion of ship overhauls. The process of creating these schedules is complicated and time-intensive, partly due to the process of assigning dependencies between work activities to avoid scheduling conflicts. The objective of this thesis was to develop a program to demonstrate the feasibility of using automation to reduce the creation time for overhaul schedules, specifically for Navy vessels.
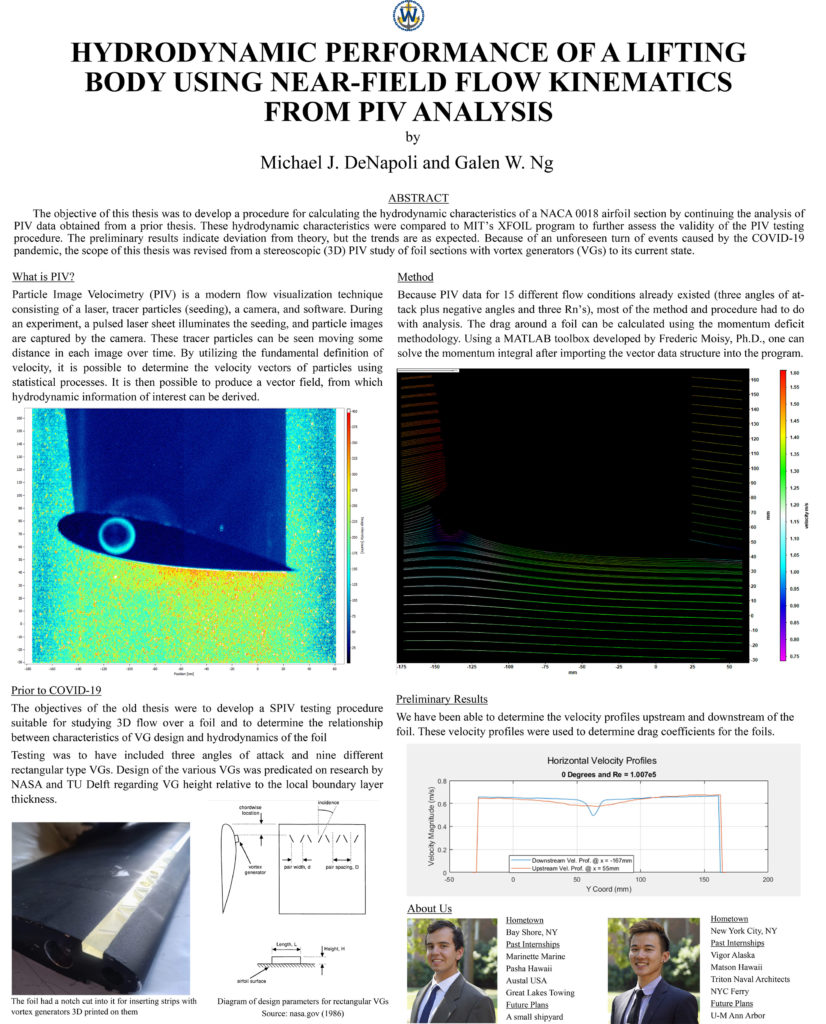
Hydrodynamic Performance of a Lifting Body Using Near-Field Flow Kinematics from PIV Analysis
Michael DeNapoli and Galen Ng
Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) is a modern flow visualization technique that produces quantitative data on the kinematics of flow fields. The objective of this thesis was to develop a procedure for calculating the hydrodynamic characteristics of a lifting body using flow kinematics data. These hydrodynamic characteristics were compared to MIT’s XFOIL program to further assess the validity of the PIV testing procedure developed in a prior thesis (Heitman, 2019). Flow kinematics were analyzed at various Reynolds numbers and angles of attack. Because of shelter-ins, the scope of this thesis was revised from a stereoscopic (3D) PIV study of foil sections with vortex generators (VGs) to its current state.
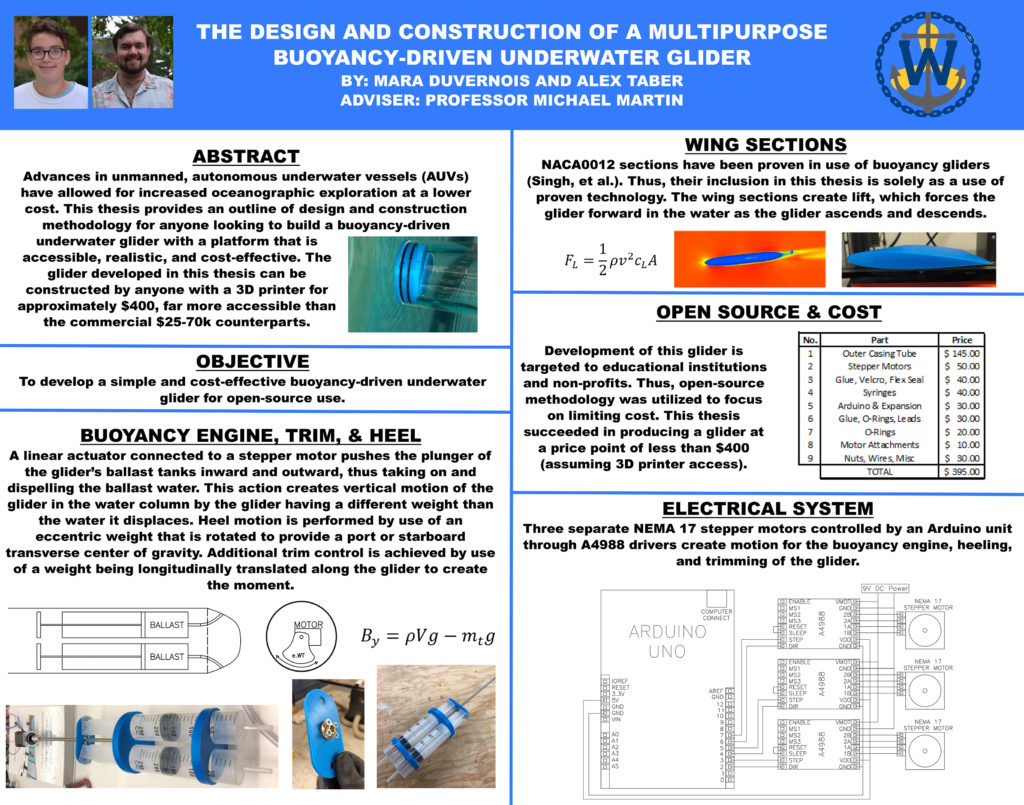
The Design and Construction of a Multipurpose Buoyancy-Driven Underwater Glider
Mara Duvernois and Alex Taber
The exploration and observation of the ocean in the past has been limited to relatively high-cost manned vessels. Consequently, this research has been limited in scope and application. Advances in unmanned exploratory vessels, such as small unmanned autonomous underwater vessels (AUVs), allow for oceanographic exploration and vessel deployment covering a larger ocean area at lower costs. The objective of this thesis is to develop a buoyancy-driven underwater glider for open-source use in a simple and cost-effective method. The glider will be a platform for future theses to further develop the autonomy of the glider, install necessary sensors, and test its data-gathering capabilities.
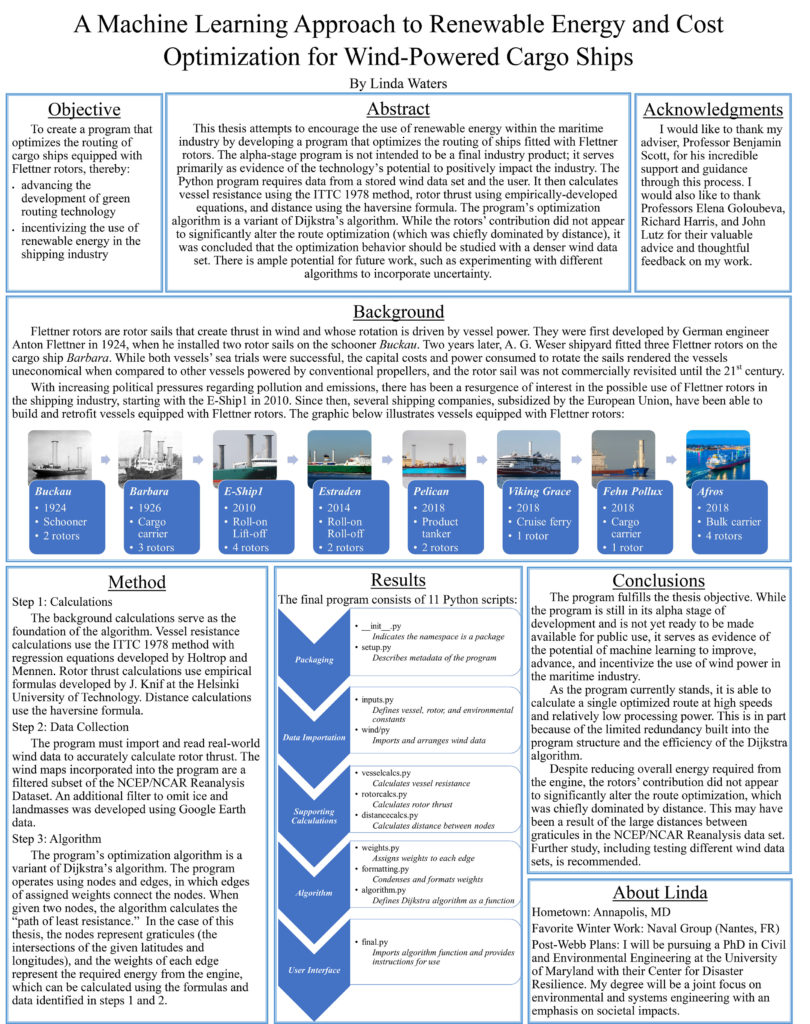
A Machine Learning Approach to Renewable Energy and Cost Optimization for Wind-Powered Cargo Ships
Linda Waters
In an effort to reduce emissions and move toward renewable energy resources, a number of naval architecture firms and shipping companies are pursuing the concept of wind-powered and wind-power-supplemented commercial vessels. However, because the modern commercial applications of sail power are still relatively new, optimal routing for these vessels remains unexplored. The objective of this thesis is, using machine learning, to derive a formula to optimize, based on energy consumption and cost, the port-to-port routing of large commercial vessels equipped with Flettner rotors.
The Development of a Model for Autonomous Vessel Path Planning
Brandon Wui
Autonomous surface vessels are increasingly being used in certain oceanographic, oil, and defense applications because of their reduced costs for time-intensive tasks such as seafloor surveying and coastline patrolling operations. One important aspect of autonomous vessel development, which often requires extensive software development work before vessel delivery, is the tuning of control, guidance, and navigation systems for vessel path planning. The objective of this thesis is to create a more accurate autonomous vessel simulator to allow developers to more rapidly tune vessel path planning algorithms.
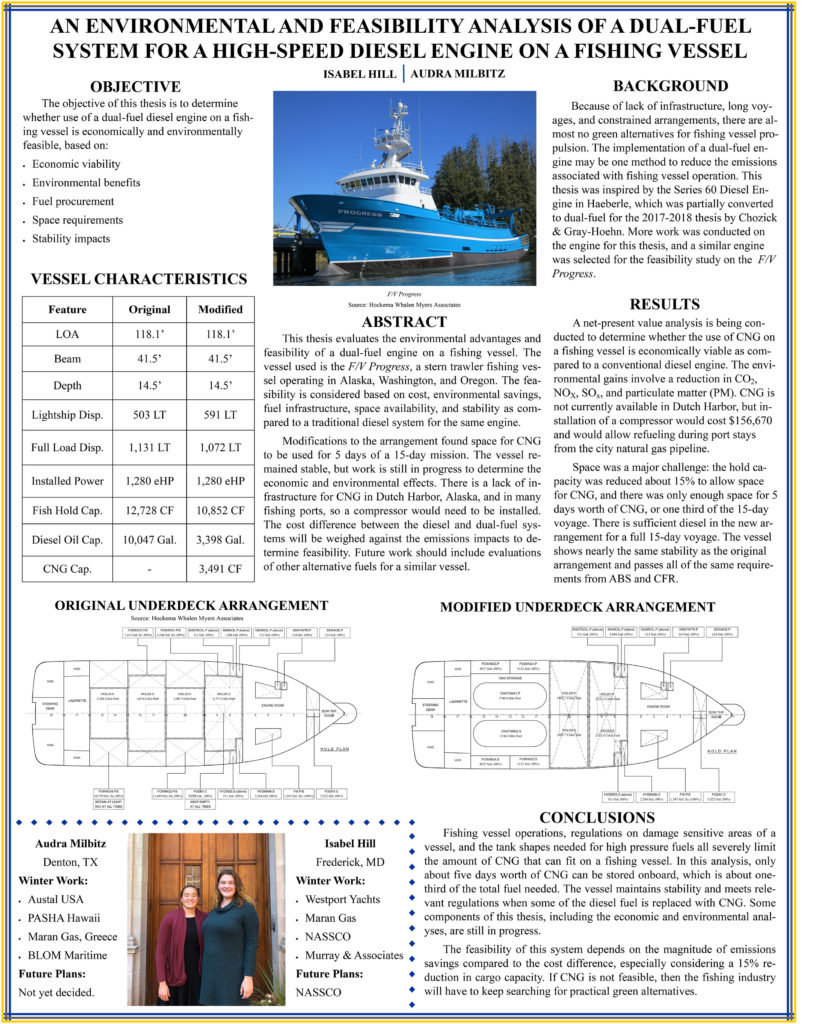
An Environmental and Feasibility Analysis of a Dual-Fuel System for a High-Speed Diesel Engine on a Fishing Vessel
Isabel Hill and Audra Milbitz
There is a demonstrated need throughout the marine industry for alternative energy options, which includes the implementation of dual-fuel conversions on diesel engines. This thesis will evaluate the performance and emissions characteristics of a Series 60 diesel engine, converted to run on compressed natural gas (CNG). This evaluation, along with research on existing infrastructure and powering demands, will be used to determine the feasibility of such conversions on fishing vessels operating off the coasts of Alaska and the west coast of the United States.
A Technical Description and Comparison of Renaissance Period Venetian Ship Construction to Liberty Ship Construction
Christopher Bal and Harrison Tack
For this thesis, we will be evaluating the 15th-Century Venetian ship construction methods of the Arsenale and determining how assembly-line practices allowed the Venetian empire to produce ships with unprecedented speed. Yard infrastructure and ship arrangements will be researched and conclusions drawn on the factors that supported the success of the Venetian empire for over six centuries. An analysis will be performed to compare Venetian methods to more modern methods of ship construction.
Video Presentation Unavailable.
Design and Development of a Small Craft Collision Avoidance System
John Grantham Dixon
In 2017, the United States Coast Guard counted 4,291 recreational boating accidents that involved 658 deaths and approximately $46 million dollars in losses. It is possible that a relatively cheap and effective collision avoidance system could be developed to help prevent a number of such accidents. This thesis explores the feasibility of such a system by developing one, and installing and testing it on Webb’s Boston Whaler.
A Thermodynamic Exergy Analysis to Optimize a Combined Brayton-Rankine Cycle
Matthew Migliozzi
With continuous need for more efficient power generation cycles, greater attention is needed to ensure that peak efficiency is achieved from all cycles. The objective of this thesis is to utilize principles from the second law of thermodynamics to determine an optimal Brayton-Rankine Cycle from the perspective of minimizing available energy destruction. The thesis will analyze a myriad of varied cycle configurations. System components which create the largest losses will be focused on.
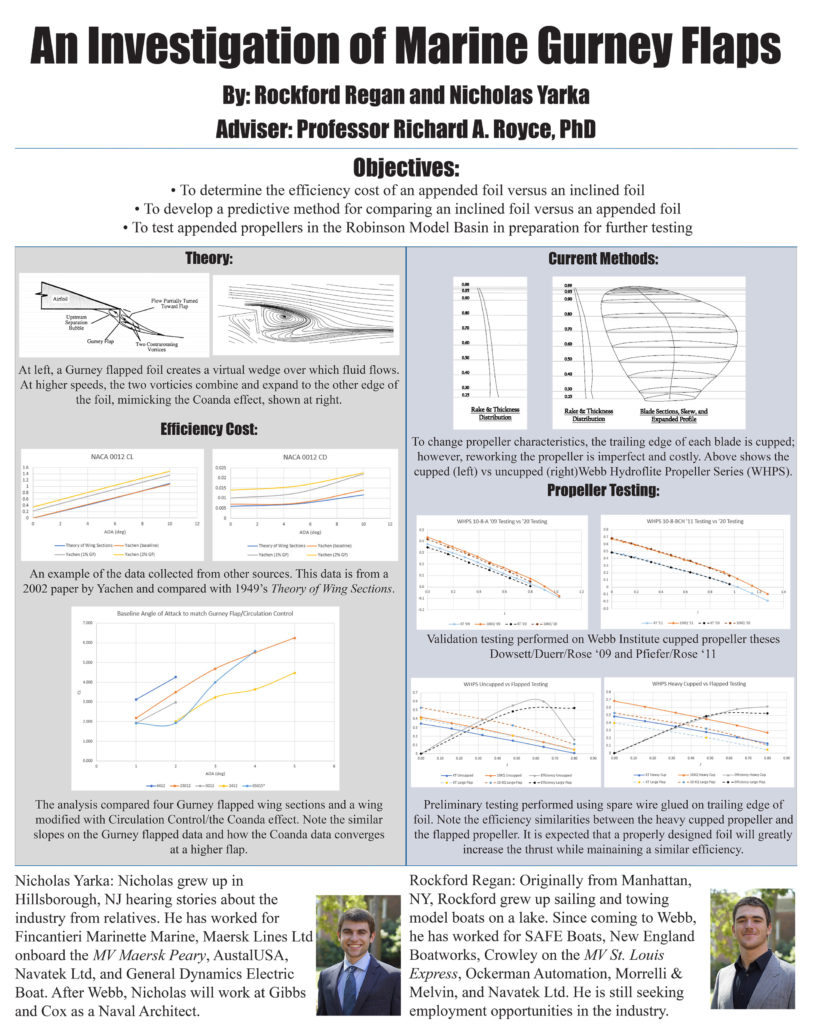
An Investigation of Marine Gurney Flaps
Rockford Regan and Nick Yarka
Gurney flaps have been used in the aerospace and race car industries since the early 1970s as a cheap and simple way to improve or change flow characteristics of wings. Recently, Gurney flaps have expanded into the marine field as a way to change propeller characteristics; however, there are no publicly available data on the performance of propellers modified this way. This thesis identifies the performance effects of Gurney flaps on propeller thrust and efficiency, with a focus on the open-water region.
Concept Design of a Floating Home: Adapting to Sea Level Rise in the California Bay Area
Mary McGuinness
Rising sea levels resulting from global climate change present a significant risk to coastal populations. The California Bay Area in particular is identified as a housing risk hotspot because of the density of the population facing exposure to chronic inundation by the year 2045. The objective of this thesis is to develop a concept design for a floating home that offers Bay Area residents survivability that cannot be attained from a traditional land-based home. An additional area of focus will be the incorporation of green features to limit environmental impact and ensure home sustainability.
Design Guide for a Modular Flexible Research Vessel
Abrianna Reddy
The current NOAA fleet has several ships operating beyond their service lives, and in the next eight years a large percentage of their research capacity will be lost. It is not feasible to conduct a one-to-one replacement of these ships in such a short period of time. A modular flexible ship design may be a solution for this problem. Making a research vessel more flexible allows the ship to adapt to changing research needs, requirements, and technology; a single flexible ship can be designed to fulfill the missions of multiple standard ships. Ship designs incorporating a high level of modularity are predominantly applied to naval ships; this type of design is new to research vessels. This thesis analyzes how modularity and flexibility can best be incorporated to a research vessel design, and provides a design guide based on this analysis.